GCC (GNU Compiler Collection)A Brief History and Introduction to GCCThe original GNU C Compiler (GCC) is developed by Richard Stallman, the founder of the GNU Project. Development Tools downloads - GCC by Free Software Foundation, Inc and many more programs are available for instant and free download. Homebrew: On the newer Macbooks with the Apple M1 processor, look for g in /opt/homebrew/Cellar/gcc instead of /usr/local/Cellar/gcc.
How do I use GCC compiler on Mac?
In OS X, GCC is part of Xcode’s command tools, so first, open the Mac App Store and install Xcode for free. Then, open Xcode, go to Xcode menu (on the menu bar) > Preferences > Downloads, and install Command Line Tools. You will get commands like gcc, make, purge…
How do I use GCC instead of clang on Mac?
You have two options:
- Create an alias.
- Make a new gcc symlink under /usr/local/bin/ . Homebrew links own gcc under /usr/local/bin/gcc- for compatibility. So, doing. ln -sf /usr/local/bin/gcc-4.9 /usr/local/bin/gcc.
How do I get GCC on my Mac?
How to install gcc compiler on Mac OS X
- Solution. To install gcc compiler on Mac OS X, you need to download and install “Command Line Tools for Xcode”, which is available in Apple’s developer page.
- Register Apple Developer Account.
- Command Line Tools for Xcode.
- Installation.
- Verification.
How do I update PIP in Vscode Mac?
To upgrade pip on mac, you can use the sudo pip install –upgrade pip command. You can also upgrade Python to get the latest version of pip om mac, windows.
How do I get the latest PIP?
Download the get-pip.py file and store it in the same directory as python is installed. Change the current path of the directory in the command line to the path of the directory where the above file exists. and wait through the installation process. Voila! pip is now installed on your system.
What is difference between PIP list and PIP freeze?
pip list. freeze Output installed packages in requirements format. list List installed packages.
How do I generate PIP requirements?
Project setup
- Create a virtual environment $ python3 -m venv /path/to/new/virtual/env.
- Install packages using $pip install command.
- Save all the packages in the file with $ pip freeze > requirements. txt.
- Pin all the package versions.
- Add requirements.
Where does PIP freeze save requirements?

pip freeze outputs the package and its version installed in the current environment in the form of a configuration file that can be used with pip install -r .
What is PIP freeze command?
So pip freeze is a command that allows you to see what modules you have installed with the pip install command to this point. So you can see all of the modules that I’ve installed using the pip install command on my windows command prompt and the versions of those modules.
Does PIP freeze show dependencies?
Project description Since pip freeze shows all dependencies as a flat list, finding out which are the top level packages and which packages do they depend on requires some effort.
What is Python freeze?
Freeze is a “pure Python” utility that ships with Python. You can use Freeze to compile executables for Unix systems. If you want to write Python, but you don’t know if your clients have Python installed, use this!
Can I compile Python to exe?
Yes, it is possible to compile Python scripts into standalone executables. PyInstaller can be used to convert Python programs into stand-alone executables, under Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, Solaris, and AIX.
Can you run Python script without Python installed?
Yes, you can run a Python script without actually installing Python on Windows with Docker .
How do I run a Python script from another computer?
1 Answer
- Download Portable Python in Folder here.
- (Optional for additional packeges used) Place venv(Python Virtual Enviroment) in same folder.
- (Optional) Use venv with python.exe -m venv env.
- Open cmd in folder with python.exe.
- Run your script with python.exe script.py.
Will PyCharm work without Python?
You need at least one Python installation to be available on your machine. For a new project, PyCharm creates an isolated virtual environment: venv, pipenv, or Conda. As you work, you can change it or create new interpreters.
Can a Python program run on any computer?
Python programs need a Python interpreter and usually a set of modules to be installed on the computer system. This stand-alone executable can be run on every computer that has the same type of operating system and the same chip type.
What program do you use to run Python?
A widely used way to run Python code is through an interactive session. To start a Python interactive session, just open a command-line or terminal and then type in python , or python3 depending on your Python installation, and then hit Enter . Here’s an example of how to do this on Linux: $ python3 Python 3.6.
What program do I need to run python?
The Easiest Way to Run Python
- Download Thonny IDE.
- Run the installer to install Thonny on your computer.
- Go to: File > New. Then save the file with . py extension.
- Write Python code in the file and save it. Running Python using Thonny IDE.
- Then Go to Run > Run current script or simply click F5 to run it.
What software is required to run Python?
One of the best (and only) full-featured, dedicated IDEs for Python is PyCharm. Available in both paid (Professional) and free open-source (Community) editions, PyCharm installs quickly and easily on Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux platforms. Out of the box, PyCharm supports Python development directly.
Setting up gcc / OpenMP on OSX (Homebrew edition)
Let's launch a new instance of Terminal, and then we type the command again: gcc -version And this time, we get version information. One interesting tidbit is that we haven't installed gcc. Instead, we installed C-line but it's pretending to be gcc. But for our purposes, it doesn't matter. We have a compiler installed and available from the. More importantly, if you want to develop for OS X, sooner or later you'll have to write some Objective-C code, and that will have to be compiled by the Apple GCC. The only easy way to get a working installation of Apple's GCC is to install XCode, even if you later delete the IDE itself. – user57368 Jun 27 '09 at 22:37.
Gcc Compiler Download Mac Os Xforce
Note: This is part of a series of “how-to” blog posts to help new users and developers of BioFVM and PhysiCell. This guide is for OSX users. Windows users should use this guide instead. A Linux guide is expected soon.
These instructions should get you up and running with a minimal environment for compiling 64-bit C++ projects with OpenMP (e.g., BioFVM and PhysiCell) using gcc. These instructions were tested with OSX 10.11 (El Capitan) and 10.12 (Sierra), but they should work on any reasonably recent version of OSX.
In the end result, you’ll have a compiler and key makefile capabilities. The entire toolchain is free and open source.
Of course, you can use other compilers and more sophisticated integrated desktop environments, but these instructions will get you a good baseline system with support for 64-bit binaries and OpenMP parallelization.
Note 1:OSX / Xcode appears to have gcc out of the box (you can type “gcc” in a Terminal window), but this really just maps back onto Apple’s build of clang. Alas, this will not support OpenMP for parallelization.
Note 2: In this post, we showed how to set up gcc using the popular MacPorts package manager. Because MacPorts builds gcc (and all its dependencies!) from source, it takes a very, very long time. On my 2012 Macbook Air, this step took 16 hours. This tutorial uses Homebrew to dramatically speed up the process!
Note 3: This is an update over the previous version. It incorporates new information that Xcode command line tools can be installed without the full 4.41 GB download / installation of Xcode. Many thanks to Walter de Back and Tim at the Homebrew project for their help!
What you’ll need:
- XCode Command Line Tools: These command line tools are needed for Homebrew and related package managers. Installation instructions are now very simple and included below. As of January 18, 2016, this will install Version 2343.
- Homebrew: This is a package manager for OSX, which will let you easily download and install many linux utilities without building them from source. You’ll particularly need it for getting gcc. Installation is a simple command-line script, as detailed below. As of August 2, 2017, this will download Version 1.3.0.
- gcc (from Homebrew): This will be an up-to-date 64-bit version of gcc, with support for OpenMP. As of August 2, 2017, this will download Version 7.1.0.
Main steps:
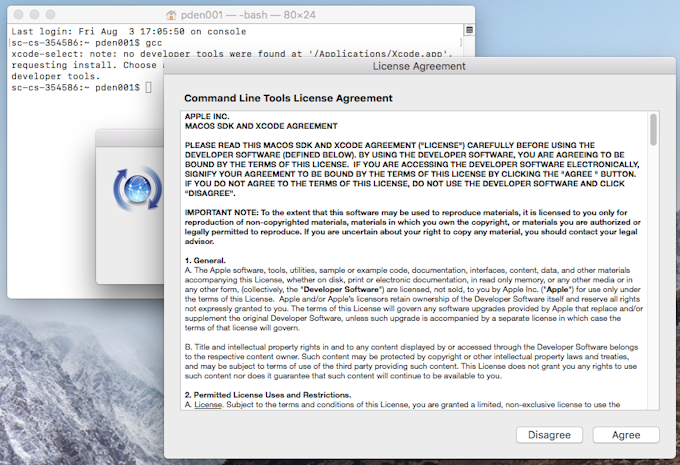
1) Install the XCode Command Line Tools
Open a terminal window (Open Launchpad, then “Other”, then “Terminal”), and run: Download lync client 2013 for mac.
A window should pop up asking you to either get Xcode or install. Choose the “install” option to avoid the huge 4+ GB Xcode download. It should only take a few minutes to complete.
2) Install Homebrew
Open a terminal window (Open Launchpad, then “Other”, then “Terminal”), and run: How to download spigot on mac.
Let the script run, and answer “y” whenever asked. This will not take very long.
3) Get, install, and prepare gcc
Open a terminal window (see above), and search for gcc, version 7.x or above
You should see a list of packages, including gcc7. (In 2015, this looked like “gcc5”. In 2017, this looks like “[email protected]”.)
Then, download and install gcc:
This will download whatever dependencies are needed, generally already pre-compiled. The whole process should only take five or ten minutes.
Lastly, you need to get the exact name of your compiler. In your terminal window, type g++, and then hit tab twice to see a list. On my system, I see this:

Look for the version of g++ without an “mp” (from MacPorts) in its name. In my case, it’s g++-7. Double-check that you have the right one by checking its version. It should look something like this:
Notice that Homebrew shows up in the information. The correct compiler is g++-7.
PhysiCell Version 1.2.2 and greater use a system variable to record your compiler version, so that you don’t need to modify the CC line in PhysiCell Makefiles. Set the PHYSICELL_CPP variable to record the compiler you just found above. For example, on the bash shell:
One last thing: If you don’t update your paths, make will may fail as it continues to combine Apple’s “gcc” toolchain with real gcc. (This seems to happen most often if you installed an older gcc like gcc5 with MacPorts earlier.) You may see errors like this:
To avoid this, run:
Note that you’ll need to open a new Terminal window for this fix to apply.
4) Test your setup
I wrote a sample C++ program that tests OpenMP parallelization (32 threads). If you can compile and run it, it means that everything (including make) is working! :-)
Make a new directory, and enter it
Open Terminal (see above). You should be in your user profile’s root directory. Make a new subdirectory called GCC_test, and enter it.
Grab a sample parallelized program:
Download a Makefile and C++ source file, and save them to the GCC_test directory. Here are the links:
- Makefile: [click here]
- C++ source: [click here]
Note: The Makefiles in PhysiCell (versions > 1.2.1) can use an environment variable to specify an OpenMP-capable g++ compiler. If you have not yet done so, you should go ahead and set that now, e.g., for the bash shell:
Compile and run the test:
Go back to your (still open) command prompt. Compile and run the program:
The output should look something like this:
Note 1: If the make command gives errors like “**** missing separator”, then you need to replace the white space (e.g., one or more spaces) at the start of the “$(COMPILE_COMMAND)” and “rm -f” lines with a single tab character.
Note 2: If the compiler gives an error like “fatal error: ‘omp.h’ not found”, you probably used Apple’s build of clang, which does not include OpenMP support. You’ll need to make sure that you set the environment variable PHYSICELL_CPP as above (for PhysiCell 1.2.2 or later), or specify your compiler on the CC line of your makefile (for PhysiCell 1.2.1 or earlier).
Now, let’s verify that the code is using OpenMP.
Open another Terminal window. While the code is running, run top. Take a look at the performance, particularly CPU usage. While your program is running, you should see CPU usage fairly close to ‘100% user’. (This is a good indication that your code is running the OpenMP parallelization as expected.)
What’s next?
G++ For Mac
Download a copy of PhysiCell and try out the included examples! Visit BioFVM at MathCancer.org.
- PhysiCell links:
- PhysiCell Method Paper at bioRxiv: https://doi.org/10.1101/088773
- PhysiCell on MathCancer: http://PhysiCell.MathCancer.org
- PhysiCell on SourceForge: http://PhysiCell.sf.net
- PhysiCell on github: http://github.com/MathCancer/PhysiCell
- PhysiCell tutorials: [click here]
- BioFVM links:
- BioFVM announcement on this blog: [click here]
- BioFVM on MathCancer.org: http://BioFVM.MathCancer.org
- BioFVM on SourceForge: http://BioFVM.sf.net
- BioFVM Method Paper in BioInformatics: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv730
- BioFVM tutorials: [click here]